Black Box Deconstruction - Control Systems
Reverse-engineered unknown dynamic systems through experimental identification, designed stable PID controllers.
Course project for MTHE393 at Queen's University. Given an unknown "black-box" dynamical system, the objective was to reverse-engineer its transfer function and design a controller meeting strict performance targets.
Grade: A+ | Role: Primary technical contributor
Problem Context
Ships experience roll motion in rough waters, causing passenger discomfort, cargo instability, and increased fuel consumption. The goal was to design an autonomous stabilization system using fin stabilizer actuation controlled by gyroscopic roll angle sensors.

System Architecture
The control system uses a feedback loop with PID control and feedforward gain compensation to stabilize roll angle.
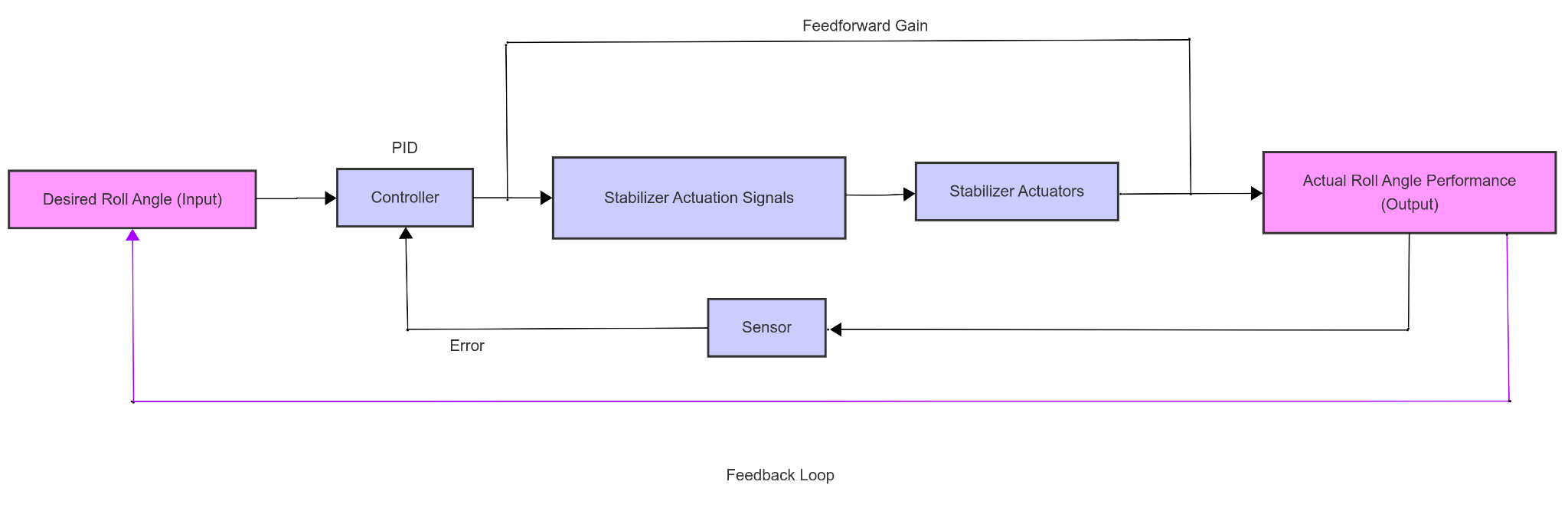
Technical Approach
1. LTI System Validation
Before attempting identification, rigorously validated the black-box was Linear Time-Invariant:
- Homogeneity: Verified H(2x(t)) = 2H(x(t)) with 0.9997 correlation
- Superposition: Verified H(x₁+x₂) = H(x₁) + H(x₂) with 0.9998 correlation
- Time-Invariance: Confirmed identical responses under time shifts (RMSE = 0.0000)
2. Signal Processing & Noise Removal
The black-box produced extremely noisy outputs requiring sophisticated denoising:
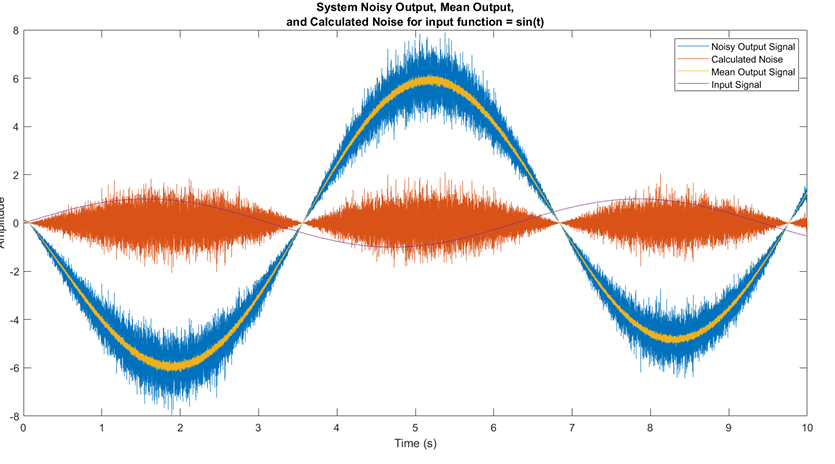
- Evaluated low-pass, high-pass, Gaussian, Chebyshev, and moving-average filters
- Final approach: Pointwise averaging of 20-100 signals per frequency
- Statistical analysis confirmed zero-mean Gaussian noise (μ ≈ 0.0015)
3. Bode Plot Construction & Transfer Function Derivation
Systematic frequency response characterization across 10⁻³ to 10⁴ Hz:
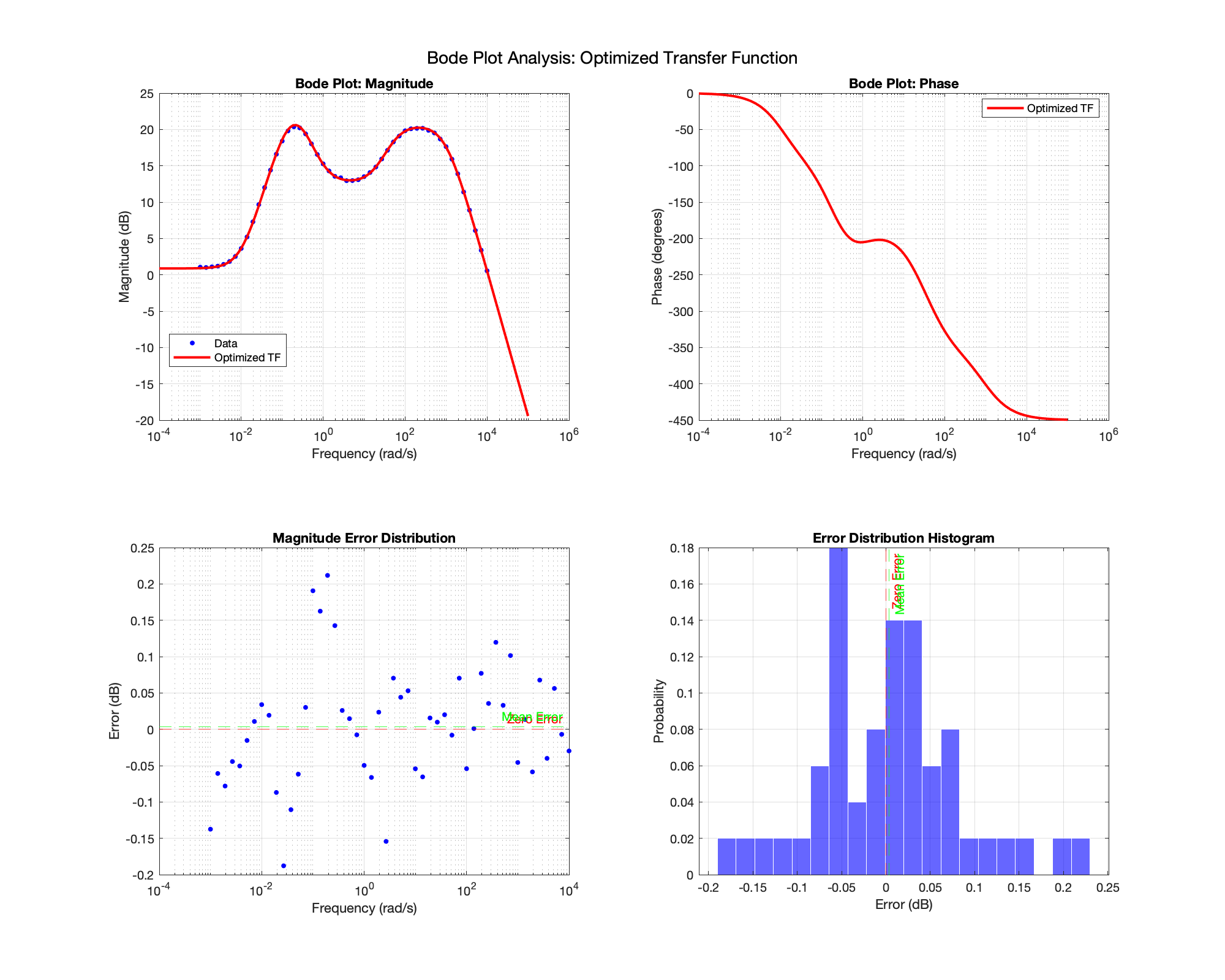
- Averaged 20 signals over 50 trials per frequency point
- Used 6 periods per signal to ensure steady-state response
- Derived transfer function coefficients through RMSE optimization
4. Controller Design & Results
Designed PID controller with feedforward compensation (L=4010) to move RHP zeros to LHP for stability:

| Metric | Target | Achieved |
|---|---|---|
| Rise Time | 1 s | 0.328 s |
| Overshoot | 1.9 | 1.005 |
| Settling Time | 3 s | 0.58-1.37 s |
| Steady State Error | ±0.05 | 0.002 |
All performance specifications exceeded with significant margins.
Skills Demonstrated
- System Identification: Reverse-engineering unknown systems from I/O data
- Signal Processing: Statistical averaging, filter design, noise characterization
- Frequency Domain Analysis: Empirical Bode plot construction
- Control Theory: LTI validation, PID tuning, pole-zero stability analysis
- MATLAB/Simulink: Simulation, optimization, data visualization
Relevance to AI/ML
This project demonstrates skills directly transferable to AI systems work:
- System identification parallels understanding model behavior from observations
- Empirical validation methodologies apply to ML model evaluation
- Feedback control design relates to RLHF and alignment techniques
- Rigorous experimental protocols for characterizing complex systems